CLICK THIS TO STOP TRYING TO ACHIEVE YOUR GOALS BY YOURSELF AND BE COACHED TODAY HERE
CLICK THIS TO DOWNLOAD THIS FREE PDF SUMMARY HERE
CLICK THESE FOR THE FOLLOWING Book | Summaries | Course
YouTube |Spotify | Instagram | Facebook | Newsletter | Website
The Art of Hunting Humans is a 2019 Readers’ Favorite Silver Medal Winner!
The Art of Hunting Humans presents key aspects of the human mind. With straightforward language, weird metaphors and practical examples, it enables readers to understand human behaviour and evaluate their lives from an outsider’s perspective.
Designed to challenge rather than comfort, The Art of Hunting Humans sets itself apart from anything else written in its field. The result is a sceptical, radical explanation of the mind that provides extraordinary insights into the inner worlds of human beings.
Book Blurb
The age-old art of human hunting is one you must orchestrate with care. In The Art of Hunting Humans, you’ll learn essential facts about Earth’s smartest primate and discover mistakes that are common among hunters while in pursuit of their prey.
Whether you are an experienced hunter or a novice, this guide is essential reading. In it, you’ll learn the major steps for a hunt — from correct observation and selection of your prey to choosing the tastiest bait. It will reveal how to leverage humans’ self-ignorance and strange behaviours and expose flaws of which they are oblivious. At the end of the book, you will have the opportunity to meet the SUPERIORS — creatures like no other. You’d better be ready!
Even if you’re a seasoned hunter, The Art of Hunting Humans provides extraordinary insights into human behaviour as well as tips that will blow your mind.
Almost everything in this book is a trap. Enjoy!
1: INTRODUCTION – EXPLORING HUMAN IGNORANCE & FLAWS
Nothing compares to the thrill of chasing the perfect prey. Hunting socially sophisticated primates, known as human beings, is the ultimate mission any creature can pursue — the most challenging and fascinating journey one can take.
Human beings are planet Earth’s smartest and most dangerous animals.
Due to the complex human central-intelligence system, human behaviour is more sophisticated than that of all other Earth-born creatures.
When hunting humans, there are many weaknesses you can exploit. Here are two:
Just like dogs
A fundamental feature to play with is the trust that humans have in their emotions, feelings, sensations — or whatever you want to call those things. This trust provides a big opportunity.
Why? Well, because humans don’t realise that their brains train them like a human would train a dog.
Fear is gold
To manipulate a human, you can intimidate him by using fear, or you can enthral him by playing with his vanity.
A human’s need for social approval is one of the easiest to manipulate.
Thirdly, humans are often deeply emotionally invested in preserving their ignorance of unsettling truths.
Among humans, ignorance is widespread.
KNOW YOUR PREY
Finally, Sun Tzu, one of Earth’s most famous practitioners of war, once said: “Know the enemy and know yourself; in a hundred battles you will never be in peril.”
‘Know the enemy’. This is the key. You must take the time to observe your prey and know it better than it does.
2: ROADMAP & WARNINGS – A GUIDE TO THIS BOOK
It is essential that you alter how you view human beings. YOU MUST make something of a paradigm shift, which can be harder than you think. Forget everything you know about humans and start from scratch. To help you to change your mindset and attitude, we will start with some basic concepts.
3: JUST CODES – A BROKEN COMMUNICATION SYSTEM
If we fully understand how inefficiently humans communicate with one another, we can use this knowledge against them.
To show you how important this is, during wars, one side will often target its opponent’s communication channels to isolate, divide and mislead. So, when hunting, understanding the intricacies of your prey’s communication is vital.
WORDS, FLAGS & SMOKE SIGNALS
ALL ARE JUST INEFFICIENT SETS OF CODES
Language is merely a translation into words of the images inside a human’s head. However, because communicating in one’s ‘mother tongue’ feels natural, humans have a hard time accepting that words are vague facsimiles of what they want to express.
Humans often think that they are explaining themselves completely because it feels natural — they are accustomed to the code.
The codes humans use to communicate are highly inefficient, like old submarines that transmit Morse code to each other. Of course, one craft won’t be able to express everything that is happening inside its shell. So, in the same way, no human can express himself fully, even though they all like to think they can. So, when humans filter rough codes from other humans, it’s easy to understand why there is so much confusion on planet Earth.
4: ALTERNATIVE REALITIES – INSIDE THE CABIN
What humans don’t realise is that when their central system (brain) receives information (from eyes and ears), like the lookout and messenger, it makes ‘best guesses’ about what the information means and what to send to their Captain.
What a human sees and notices is slightly different to the others around him. This is because what a human sees, hears or smells isn’t reality; instead, it is a hugely filtered best guess of what is real. Consequently, every human being’s interpretation of reality is different. It is interpreted and replayed inside his head, like a hallucination.
Each human’s brain projects different images inside his head.
Each human lives in a different reality because their brain translates information from their senses differently.
DIFFERENT REALITIES CAN EXPAND TO SITUATIONS
THE WORLD OUTSIDE IS TOO COMPLICATED,
SO HUMANS WORK WITH LIMITED INFORMATION
BUY THE BOOK HERE
CLICK THIS TO STOP TRYING TO ACHIEVE YOUR GOALS BY YOURSELF AND BE COACHED TODAY HERE
CLICK THIS TO DOWNLOAD THIS FREE PDF SUMMARY HERE
CLICK THESE FOR THE FOLLOWING Book | Summaries | Course
YouTube |Spotify | Instagram | Facebook | Newsletter | Website
In truth, when humans know or care about something, they see more.
The brain doesn’t inform a human of everything; it chooses what to report and the amount of detail.
Most information captured is simply ignored
For example, humans are well aware that during a stage, which they call “being in love”, a love-struck human often alters his reality and, so, is unable to spot defects in his partner (or he simply minimises their importance). So, humans are sort of aware of this phenomena. However, what they fail to acknowledge, and where an opportunity arises for us, is that humans distort reality continuously and at much deeper levels than they think.
Every day a human is exposed to an avalanche of information, and only a fraction will reach his awareness.
THE POWER OF THE MESSENGER
The Messenger decides what the Captain should be aware of (or not) and how the message should get to him.
And, if you think about it, you will realise the enormous influence the Messenger has; he controls which information the Captain receives, and he chooses how it’s delivered. In effect, the Messenger can adjust the narrative to influence the Captain’s decision. And one of the crucial elements of a great deception is to convince your victim that he is in control.
A human’s reality isn’t shaped by just culture, knowledge or experiences. He also sees things differently depending on his mood.
THE CAPTAIN IS ALWAYS INSIDE THE CABIN
Always
The key thing to understand is that every human sees the world from inside his head — the Captain’s Cabin. Everything is a replication of what is going on outside.
Basically, humans live in a constant hallucination — like they are wearing virtual-reality goggles.
If you can manipulate sensations that humans love by replicating them inside their heads, you will have the power to shape them without needing the object.
While many things can hurt a human, they are limited by reality. The number of possible dangers, however, that a human is afraid of is several times greater because of the magnifying power of his imagination.
TAKEAWAYS FROM THIS CHAPTER
For a human being, his perception of reality is often uncomfortable, so his ever-vigilant brain suppresses and alters reality to protect his fragile Captain. Yes, the Messenger tricks the Weak Captain to avoid additional problems.
Needing to blame others is usually a sign of weakness.
You will often see humans attempt to protect themselves in this way, even though doing so should be embarrassing.
This idea of humans creating alternative realities isn’t easy to accept, but it will make it much easier for you to understand the curious and abnormal behaviour of your prey.
As you will observe, a large portion of humans are immune to reason and facts, and it is not unusual for them to deny problems exist if they don’t like the consequences. And, if a human wishes to change another human’s mind, providing more information to support an argument won’t help.
As a rule of thumb, if your human prey doesn’t like the outcome of something, he will usually question the problem and deny it existed in the first place. This way he doesn’t have to deal with the consequences. Often, his denial will be at the Messenger’s, not the Captain’s, level. So, he’ll truly believe in what he says. We kid you not!
Don’t ever offer solutions for the problem your prey complains about; if you do, it won’t help you manipulate him. In these cases, humans are usually immune to reason and don’t want a solution;
When you see a human in denial or blaming others, don’t interrupt.
Remember this quote by one of Earth’s greatest warmongers:
“Never interrupt your enemy when he is making a mistake” — Napoleon Bonaparte.
5: THE ISOLATED CAPTAIN – FIRST TIPS
The first practical application
REPETITION
With the Captain-in-the-cabin mindset, it is easy to understand why humans are usually condemned, fated — cursed — to repeat the same mistakes endlessly.
When you begin observing and hunting humans, you will notice that they often face the same problems time and time again.
What makes humans so dysfunctional?
From what we have presented until now, a human’s filtered reality (his ability to notice certain things and his selective attention) is a culprit.
First – Alternative Reality: Every individual human being will tend to pay attention to things — objects and situations — that others may not be aware of or care about. Also, based on each human’s background and experience, they can notice different things and details while in the same situation. So, as previously said, humans see reality differently. Remember, reality is complex, so there is always something happening around humans that allow them to reach the conclusions that they desire.
Humans see what they look for and understanding this fact will help you recognise the problems they face.
Secondly – Desire: Each human has a pattern of desire, so he is attracted to and finds pleasure in the same things. Without noticing, humans usually chase the same type of humans over and over again. So, it’s often their desire — what they chase — that creates the reoccurring problems humans complain about.
Thirdly – Behaviour: Without noticing, humans also create problems by the way they behave.
Humans can’t comprehend that, most often, they are the architect of their problems.
Another practical application
LISTEN TO THE WORDS OF YOUR PREY
A human’s words expose the core of his reality and reveal a glimpse of what information he pays attention to and how he filters it.
The 3 levels of the funnel:
- The captured reality that is detected by each human’s sensors (eyes, ears, etc.).
- The perceived reality (a small part of level 1) that the brain processes. This is the core — what he pays attention to.
- The commented reality (a small part of level 2), which is the part humans choose to talk about — the core of the core.
Humans grasp but a fraction of what’s going on (captured reality) and then filter it their own way (perceived reality). Then, they use this small portion to make comments (commented reality). As you can imagine, what humans talk about should expose the crumb of reality they pay attention to. However, it gets better. Knowing what a human values is essential when deciding which trap and bait to use.
Words are just a means for communicating to the world a slither of the information the Captain receives. Therefore, hunters should pay attention to what their prey says because, through their words, they are expressing the fraction of reality they see and how they see it.
BUY THE BOOK HERE
CLICK THIS TO STOP TRYING TO ACHIEVE YOUR GOALS BY YOURSELF AND BE COACHED TODAY HERE
CLICK THIS TO DOWNLOAD THIS FREE PDF SUMMARY HERE
CLICK THESE FOR THE FOLLOWING Book | Summaries | Course
YouTube |Spotify | Instagram | Facebook | Newsletter | Website
As a rule, the things one human criticises another about reveal clues for what you can use against him. When a human criticises something, he is also, in an indirect way, saying he is not that. Or, in other words, he is better than that.
Whatever a human talks about reveals what he pays attention to. Listen to what he says, and especially to what he complains about, and you will discover the best bait for your hunt.
6: HAUNTED BY MEANINGS – HIDDEN ASSOCIATIONS
So, human communication is a mess, and Earth’s smartest animals live in different realities. One consequence (among many) is that each human continues to face the same problems over and over again.
The meanings humans attach to things and situations vary widely among them and profoundly affect how they perceive their surroundings.
Humans are unaware of the associations they make.
Associations are hidden, and so humans don’t realise they ‘see’ different things.
Do you know that every human has an inbuilt codebook to decipher his environment? It’s true. And, like the messengers’ interpretations, each human’s book of codes is different. Consequently, humans appear to be talking about the same thing, but many times they are not. So, it is possible to observe completely different behaviours between humans facing the same situations.
DIFFERENT ASSOCIATIONS AT GROUP LEVEL
Let’s look at a few everyday situations:
In some parts of Earth, getting a tan is considered desirable and leads to more social approval. There, white humans sunbathe or apply artificial methods to darken their skin.
Meanwhile, in other places, chalk-white skin is considered more attractive; some humans actually inject substances into their veins to achieve this goal.
So, a human from one part of the planet (like China) will have an opposing idea of desirable skin colour than one from another part (like Brazil). Both humans share the same goal, but to look good or be sexy, one hides from the sun while the other chases it.
Skin colour can have opposite meanings for different groups of humans.
Misunderstandings happen between cultures, despite humans knowing that interpretations of things and situations can vary widely.
When hunting, aim to know, better than your prey, what things such as power or marriage represent to him.
HIDDEN ASSOCIATIONS
A discussion can be an exchange of ideas or a chance to see who is best
Read between the lines to understand what humans are really talking about.
DIFFERENT MEANINGS IN HUMAN RELATIONSHIPS
Humans are usually unaware of all the associations behind whom they find attractive — they just know they find another either ‘hot’ or not.
The thing to understand is that Hidden Associations can be radically different from human to human, but the outcome is usually powerful. Humans reach important conclusions with a minimal understanding of the reasons why. They don’t treat it as a possibility, but most often as a logical and certain conclusion.
Humans think everybody reads from the same codebook; they are confident that their, often erroneous, conclusions are correct. Just like a human who reads the wrong map and feels sure he is heading in the right direction, a wrong book of codes misleads a human’s interpretation of the world. So, often, humans’ Captains are receiving the wrong information and perceiving alternative realities.
CONTINUALLY CHANGING UNCHANGEABLE TRUTHS
Interestingly, most humans are unaware that what they believe to be universal truths have changed over time.
For example, among humans, dominance during sex is currently associated with being on top; in days gone by, however, dominating meant being beneath a partner. So, two humans who both want to be in the ‘driver’s seat’ can do so in opposite ways: one can be on top, and the other can achieve the same goal on the bottom.
So, many of the ‘truths’ humans believe are simply a product of their generation, and yet they act as if they have always been so. As a result, it becomes even more difficult for them to question the assumptions in their minds.
Tip: If a human overreacts to something, he is probably linking it to other meanings.
AN ANCIENT & ESSENTIAL FEATURE
It is important to note that Hidden Associations (or simply inner Shortcuts) are not all bad. In fact, many are necessary because they allow humans to react quickly to things and situations without expending much cerebral energy.
Though often necessary, the problem with Shortcuts is that humans are addicted to the fast, easy way of seeing the world, and they can’t kick the habit.
The human brain assigns meanings to the stuff. Not just often, but always. So, that is not just a lion; it is a predator and danger all at once.
It’s true that analysing a situation objectively is difficult and energy-intensive for humans. In modern times, though, analysis at least avoids wrong conclusions such as:
- “He refused to wash the dishes today, so he doesn’t love me.”
- “The human is poor, so he’s a loser.”
- “He’s rich, so he’s a winner.”
- “He’s gay, so he’s a freak.”
Some assumptions are essential for survival. For example, a human sees an angry dog and immediately assumes he should find a place to hide. Or, if a human sees another approaching wearing strange clothing and holding an axe, he presumes that this odd character is trouble, so he crosses the street.
Humans make assumptions based on their experiences, which, when fleeing from a lion or an axe-wielding weirdo, is a sound life-preserving strategy. However, very few humans are cognisant of the assumptions they make, and only awareness will enable them to ask questions such as, “Is wealth really an indication of intelligence?” or “Is washing the dishes a proxy for love?”
Humans make so many incorrect assumptions that they are not even aware of.
Assumptions often lead some humans to conclude that kindness is weakness and brutality is power; a want is a need and something that is common is normal, which then becomes the right thing to do.
Some humans even directly link uncertainty with danger. Most can’t see that all these associations can be both right and wrong.
By not jumping to conclusions you can uncover the truth.
One of the most intriguing and misleading conclusions humans come to is that ‘ranting and raving’, and trying to impose one’s will on others, is a sign of power. Most often, though, in a group of humans, the one who makes the most noise is the weakest and the one who feels most vulnerable. It’s true: Humans who feel compelled to demonstrate their power at higher decibels usually doubt whether they have any power at all.
As you can see, a small sign can be viewed as related to strength or weakness, depending on Hidden Associations.
Humans become masters of deception in order to avoid unpleasant experiences, and they use the techniques of denial and blame. They ignore problems and keep busy to avoid thinking about them.
It is also important to remember that all human parents were once children, so they also have a legacy of strange associations from their early years influencing them. As a result, throughout human history, there is a chain of events with cause and effect passed from generation to generation.
THE HUMAN BRAIN’S ASSOCIATIONS CAN HAVE OPPOSITE & UNEXPECTED MEANINGS
To complicate matters further, it is possible for your prey to have not just slightly different, but totally opposite, meanings related to the same thing. As usual, it all comes down to what something means to each human.
For example, feeling pain (which one would naturally expect should be avoided) can lead a human to believe he is winning. And, so, he can enjoy it. The way a human views pain can considerably change his perception of, and interaction with, reality.
You see, all kinds of links can happen. Suffering can mean something to be avoided, or it can have a good connotation.
Humans become immune to reason.
7: THE EXTREMES – HUMAN DRAWERS
As if the Hidden Associations aren’t crazy enough, here’s another reality-distorting human feature: These creatures organise information within their heads into categories — like drawers.
One small thing can transform a situation from being perceived as excellent to awful.
In this chapter, we use Drawers as a metaphor for categories. Doing so will enable us to demonstrate how an even slightly different meaning between humans can lead to massive differences in how each perceives reality.
Humans continuously categorise everything they see or pay attention to. You see, labelling things and situations helps them understand quickly what’s happening around them. But, for hunters, what’s most fascinating is that humans usually have too few categories, or Drawers, as we describe them, and so they must adapt. Yes, for many humans, their brain has minimal Drawers, so they label things based on what they have. What other choice is there? As expected, this feature causes extreme behaviour because things get stuck in the duality of 0 or 100: good or bad, black or white; there is no middle ground.
For example, if a human had just two Drawers (black and white) he would have no choice but to place any colour he sees in one of the two. So, anything that isn’t entirely white may be interpreted as black.
How does this all work in practical terms? Well, as mentioned, most humans have too few Drawers, so they label everything as either “winner” or “loser”. With only two large Drawers in their minds, these humans live in perpetual fear of being perceived by themselves, or others, as a loser.
HOW DOES LABELLING HAPPEN?
Labelling happens before humans receive information, so the message is compromised by the time it reaches the Captain.
All decisions for which Drawer to place information into (how to label and store it in a human’s memory) are made before the Captain receives it. The message is biased, tainted. Before a human truly understands a situation, his heart pounds, or he becomes angry, and all these reactions are mostly beyond his control at the time. Should the human have developed more Drawers, he would have better control.
People can present very different behaviours based on their interpretation of the occasion.
You see, to a human with just two Drawers, success means he is a winner, and a small flaw makes him a loser, afraid, unlovable and a social pariah. One Drawer holds many meanings.
You wouldn’t believe how often outwardly successful humans become disproportionately devastated by small setbacks.
Understand this: An overreaction usually indicates a small number of Drawers. You see, exaggerated emotions are often caused by extra meanings that develop because of the winner/loser way of analysing things — a small mistake meaning to a human that he is a loser. So, whenever a human overreacts to a situation, it usually indicates that he has a poor grasp of reality and probably constantly fears becoming a loser.
Labelling and categorising affects humans all the time.
Humans continuously use small clues to reach far bigger conclusions.
Tip: If a human relies on small clues, you can fabricate them and let him reach the big conclusions that you want. You can create a whole new image of yourself based on minor details that are easy to arrange. So, can you fabricate small conclusion-forming clues to enthral and intimidate a human? You bet!
Understand that if a human is extremely upset after a small mistake, it is usually because, in his mind, he has jumped from the Winner to Loser Drawer.
Humans ignore problems, using the Weak Captain’s strategies of blame and denial. Yes, these animals often deny reality because accepting they are a loser in one aspect of their life is too painful. To them, being a failure in one thing and an achiever in another isn’t possible. Blame and denial never fix the problems humans face, so they experience them over and over — it’s a never-ending cycle.
8: THE BRAIN’S PUPPET – EMOTIONS & DESIRES
THE MECHANISM
The (ancient) brain, which developed several thousand years ago, and doesn’t understand modern life or technology, calls the shots. And, without question, humans follow orders. So, if the brain instructs to be scared, angry, or anything else, the ‘puppet’ obediently follows its ‘wise’ central system.
When the Messenger (or brain) detects a potentially threatening pattern, it switches to war mode.
The human, though, might only be preparing for a class presentation.
Emotions play a crucial role in how humans behave, and humans are hardly able to question them. And, of course, the brain’s signals (emotions) are not always right.
Confront a human with the fact that his brain has been training him, and at a much larger scale (24 hours a day since birth), he will probably enter into, what we call, “denial mode”.
Humans struggle enormously to understand that what they feel is not necessarily right, wrong, or, in fact, anything at all. It is merely good or bad stuff that their central system uses to train and guide them. So, just like ‘Fido’, most humans have limited self-understanding — they are their Brain’s Puppets.
The previous examples show that the brain uses a human’s emotions to guide him to do what it believes is best — from avoiding pain, to seeking pleasure and feeling good about it.
The truth is that the human brain applies the same technique as a dog trainer; it reinforces good stuff with pleasure and the bad with pain. And, as one can expect, pain can be extremely persuasive.
The human brain, though, was designed thousands of years ago for animals clinging to survival in the jungle. Consequently, it still reinforces unnecessary behaviours — overeating sugar or fat, for example.
The essential thing to remember is that a human’s brain has been training him since birth, so most humans, like obedient dogs, are unaware of why they like some things and dislike others.
The human brain (the Messenger) creates reality, with some editing, based on what it wants the Captain to see.
The brain, training him like a puppet, also decides when to send a human pleasant or unpleasant messages.
That’s a lot of control. One could say it’s about time the Captain stopped trusting his Messenger so much and started asking questions.
DESIRES, TOO, CAN BE MISLEADING
Humans most often don’t fully understand their desires and just follow what their brains think they need.
Humans don’t question or understand their desires.
The human brain implants desires to get what it feels is needed
Humans are often just puppets?
Humans rarely question assumptions that translate into desires and emotions — they feel too real.
Hidden competition happens more than humans imagine — like between males of the same tribe (the mate and father of a female, for example) competing for dominance of the house/family. Often you can see hidden competition disguised in weird discussions and small actions.
Can you see how competition is far more prevalent in human behaviour than they can recognise and how it affects humans’ emotions and desires at a much deeper level than they know?
Humans are complicated animals, aren’t they? Their ridiculous Hidden Associations can create not just emotions, but also desires to instruct them to do what their brains believe they should. And, humans can make minor and major decisions about their careers, marriages, etc., while unaware of the real reasons why.
HUMANS’ LACK OF AN OUTSIDER’S POINT OF VIEW
Humans struggle to observe themselves from the sceptical perspective of an outsider.
Humans can only question their instincts, beliefs, emotions, Hidden Associations, if they study themselves from the sceptical perspective of an outsider, like a creature from another planet. But they hardly ever do.
Can you imagine a human about to lose his temper and then asking, “Why am I nervous? What does this situation mean to me? Should I feel this way? What can I learn from my nervousness? What does this desire mean to me? What I am really looking for here? Am I trying to escape from something?”
BUY THE BOOK HERE
CLICK THIS TO STOP TRYING TO ACHIEVE YOUR GOALS BY YOURSELF AND BE COACHED TODAY HERE
CLICK THIS TO DOWNLOAD THIS FREE PDF SUMMARY HERE
CLICK THESE FOR THE FOLLOWING Book | Summaries | Course
YouTube |Spotify | Instagram | Facebook | Newsletter | Website
Can you imagine a human questioning his emotions or desires this way? No, right?
It is beyond most humans’ capacity to study their emotions sceptically as if from outside their bodies.
Imagine a human who has never left his country. He would find it nearly impossible to question his culture, rituals (weddings, funerals, human greetings, etc.), expected social behaviours, social structures and religious beliefs.
For this human, given that he has known no other life, everything seems natural and as it should be. How could he possibly feel otherwise? Meanwhile, a foreigner would have a very different perspective and be able to evaluate these things from an outsider’s perspective.
9: PRELUDE TO THE CHAPTER ‘PERSONAL
HOLY GRAIL’ – PERCEIVED LACK OF POWER
Humans become angry or irritated (or simply feel unpleasant sensations) when they perceive that they can’t do what they need or want. You will see that when humans feel powerless, they get unpleasant sensations, and, conversely, when they get what they want, they feel in control and powerful — all pleasant sensations.
Interestingly, when a human becomes angry in his day-to-day life, he usually can’t see that the real source of his PERCEIVED LACK OF POWER or control over a situation.
Our ancient brain hates not being in control.
That’s just how the brain operates. So, it will send requests (emotions) for the human to do something about the situation, unpleasant sensations to get him out.
The source of the problem, as usual, is the perceived lack of control over a situation. Even if it doesn’t matter much.
You see, humans feel good and more powerful when they can do or get what they want, and they feel the opposite when they can’t.
Humans try to balance a minimum amount of perceived power (pleasant sensations) in their minds. As we said, lacking power is unpleasant for humans, and sometimes they compensate for the discomfort by acquiring short-term pleasure or power from other things.
For example, a human gets dumped (an unwanted divorce), so he indulges in compulsive shopping to compensate. Or, a human loses his job and kicks someone’s arse in a bar to make himself feel powerful again.
You see, in both situations, each human is trying to re-establish a perceived minimum level of power and pleasure.
PERCEIVED is the key word in our analysis because the feeling of powerlessness happens inside a human’s head.
10: PERSONAL HOLY GRAIL – VANITY
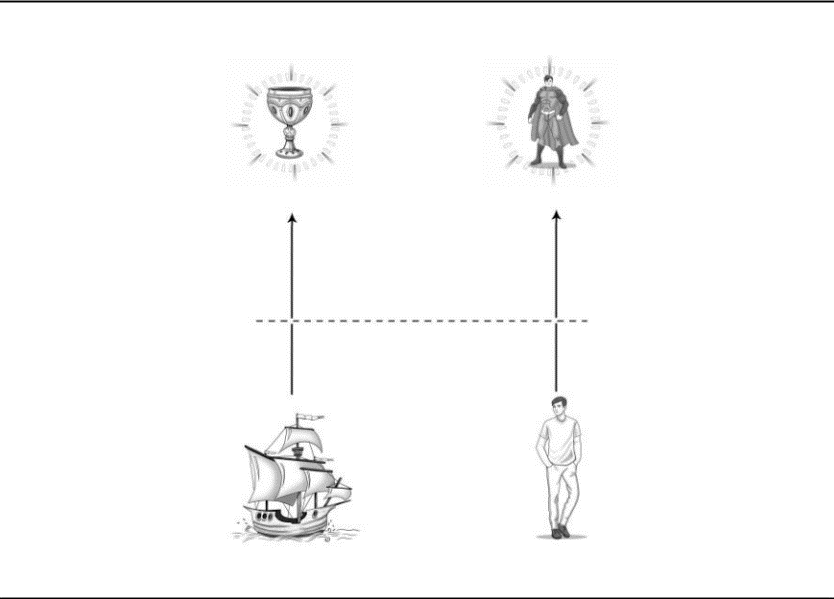
To simplify several concepts, let’s say that each human has a Line of Power. This line traverses between whom the human thinks he is (his self-image) and whom he wants to be.
By whom he wants to be, we mean a super version of himself, of what he is on a quest to become. Like the Crusaders of old, every human seeks a Personal Holy Grail — a dream, a super-self, a goal.
So, there is the Line of Power that is the route to reach the Holy Grail. Just like a ship on a mission, humans feel good when they perceive they are getting closer to their Holy Grail and bad when they perceive they are slipping farther away. Simple.
The Line of Power is the rope that links a human’s current self-image to his Holy Grail.
In general, only things that relate to a human’s Line of Power will affect him. Events outside it will usually have little or no impact.
A human’s Personal Holy Grail usually depends on a combination of traits: his beliefs, knowledge and past experiences (especially childhood), for example. It is the product of his desire to feel happier, safer and more accepted, etc.
Whatever a human’s purpose is (Holy Grail), what matters to him is whether he is getting closer to or farther away from it. And, we must point out that once a human has consolidated a goal, it is difficult to change his focus.
SO…WHAT IS SUCCESS?
The accomplishment of something (a purpose, a dream) is a simple definition of success, according to the human ‘code’. Success. It is just one word. However, look deeper, and you will see that its meaning carries a lot; every human’s idea of success differs.
Humans usually say they understand the different definitions of success, but they have enormous difficulty understanding a human that contradicts their own.
Almost all decisions humans make are based on their perceived super-self.
No matter how big the dream or how distant the Holy Grail, what matters to a human is whether or not he is moving towards it. Simple.
A human can desire whatever he wants, and his desire will define the DIRECTION he wishes to go.
Humans continuously ‘bark up the wrong tree’, so to speak, when trying to influence others.
Beliefs, such as his Hidden Associations (which include suppressed memories) and his Holy Grail, become part of a human’s identity.
Humans’ vanity is central in their lives, and it begins to form based on what they admire or are proud of.
The Holy Grail is a GOAL, but the primary influence it has on a human is the DIRECTION it leads him to take; it defines his vanity.
What makes a human feel pleasant or unpleasant sensations? It’s simple: When closer to his Holy Grail he feels good; farther away, he feels bad. And events outside a human’s Line of Power usually have little impact on his emotions.
11: VANITY – PRACTICAL TIPS
To become a great hunter takes patience.
A few helpful questions are:
- “What is the meaning of success for this creature?”
- “What is it proud of?”
- “What is its super-self like?”
Having a single, specific definition of success is extremely risky for humans; a small ‘bump in the road’ can pose a considerable threat and be devastating.
12: SCEPTICAL TO THE BONE – SELF-INTEREST EXPANDED
Every second of the day that humans work, play, relax, sleep, or do anything else, they are doing what they believe is best for them.
A human’s actions ALWAYS, ALWAYS, again, ALWAYS start with self-interest, which is the lever that drives them.
Every single human focuses on what they believe is the best for them.
Self-interest is the lever that drives all animals.
Our concept of self-interest
Three major things influence how the human brain behaves:
- Human rewards EXPANDED.
- Its desire to maximise good things and minimise the bad.
- Its capacity to consider the long-term.
13: SURVIVAL MODE – FEAR
Humans most often live in fear that they artificially create.
The brain plays with a human’s emotions to drive him towards the direction it wants. One of the most potent emotions at the brain’s disposal is fear.
Fear, is more than an emotion, though. It is an unpleasant and overpowering feeling caused by a threat (or anticipation) of danger, pain or harm. Fear is difficult to ignore. Play with fear, and you tap into the power of mother nature herself.
Fear is a reaction caused by its brain detecting that its body might be vulnerable, examples are anger, nervousness, extreme hate, frequent anxiety, high levels of stress, or sometimes even aggression.
Survival Mode always starts with dissatisfaction. There is, without fail, something lacking. So a human FEELS he NEEDS something essential and, therefore, believes he is being deprived.
The trick is that humans almost always think they NEED more than they do.
Believe it or not, humans tend to suffer more from imagination than reality by creating unnecessarily high needs for survival and being afraid of not meeting them. When humans fall below a minimum level of Resources, Alliances or Trust they switch to Survival Mode and can’t fully control themselves.
Before pursuing his Holy Grail, a human must first focus on survival. He needs to feel his life isn’t in peril. And for this to happen, a human must fulfil some minimum requirements.
BUY THE BOOK HERE
♣CLICK THIS TO STOP TRYING TO ACHIEVE YOUR GOALS BY YOURSELF AND BE COACHED TODAY HERE
♥CLICK THIS TO DOWNLOAD THIS FREE PDF SUMMARY HERE
♦CLICK THESE FOR THE FOLLOWING Book | Summaries | Course
YouTube |Spotify | Instagram | Facebook | Newsletter | Website
And, when humans lack things, they feel vulnerable, which leads to fear, anxiety, anger — losing their temper and all that stuff related to Survival Mode — which, as you know, lowers their rationality and control.
HUMANS IN SURVIVAL MODE
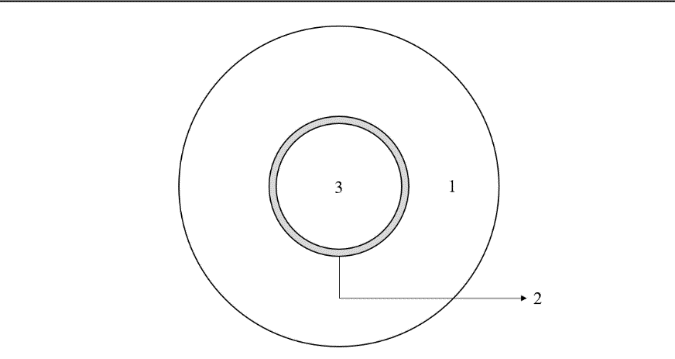
Figure 3. The minimal level of requirements.
Naturally, when below the minimal level of requirements, the brain alerts an animal that its life is in peril. Once these minimum requirements are fulfilled, though, the animal is freer to pursue its Holy Grail.
So, the main differences between the two situations are as follows:
- When a creature is above the line, he chases what he WANTS — his vanity, etc. Problems on the way usually cause some discomfort or disappointment, but nothing major.
- On the other hand, when in Survival Mode, where a creature is in desperate pursuit of what it believes it NEEDS to survive, even minor problems lead it to lose its temper and become aggressive. Anything can look threatening.
There is one big difference between humans and other animals: Humans are more able to think in the long-term. The FUTURE influences them more.
There are three factors that determine whether a human feels safe: Resources, Alliances and Trust.
There is a direct link between a need for control and perceived vulnerability. The fact that some humans NEED to feel in control at all times — omnipotent — is a sign of perceived weakness, just like inexperienced hunters need more food in the jungle. Powerful humans don’t need to feel in control; they deal with problems if and when they occur.
A lust for power — a SYMPTOM
Lust for power is an intense, insatiable desire to control everything — to be all powerful. It happens when a desire (want) for power becomes a NEED.
That humans who lust for power are trying to feel safe. Therefore, their unquenchable thirst for power and control is a SYMPTOM, an indication of a disease (a weakness). It exposes a perceived vulnerability,
Humans manufacture a persona when they flaunt status symbols to increase social acceptance. They can use fancy clothing, jewellery or, maybe, expensive sports cars to encourage others to reach favourable conclusions, to view them as successful human beings.
Therefore, a need for Alliances can easily be confused with a need for Resources because a human with more Resources, like money, will probably be more socially accepted. Make no mistake, though: The luxury goods market comprises a significant portion of consumers who have an enormous need for social acceptance because of low self-confidence.
It’s not the objects these humans seek, but the fulfilment of their basic needs. Objects are a mere means to an end. The tricky part, though, is that humans are oblivious to what’s going on, and they confuse status symbols with the goals they seek. As usual, a human’s brain uses emotions and desires to play him like a puppet. When humans acquire status symbols, they do, indeed, feel pleasure, and so they believe that the pleasant feelings are because of the object. In fact, it is their brain rewarding them for taking an action that will allow the brain to feel safer. It’s as simple as that.
As a general rule, the more a human relies on external entities, the more he is scared of losing them.
As a rule, the happier a human is with a compliment, the more he needs it. And the more he needs external reinforcement, the more insecure he is.
14: FEAR – PRACTICAL TIPS
An animal that loses its temper is vulnerable.
Some other common signs that identify vulnerable prey are:
- Obsessions — an escape to a new world
- Extreme niceness — a slave of acceptance
- Extreme Truths — a search for certainty
- Drugs — relief by ignoring bad results
15: PRELUDE – THE FOUR CHARACTERISTICS
most humans suffer from an acute lack of self-knowledge.
four characteristics of the human mind: comparison, adaptability, judgement and Rigid Rules.
16: BUILDING A CAGE – THE SURVEILLANCE SYSTEM
From childhood to adulthood, a human creates rules for behaving in society — moral standards learned from parents, religion, those in authority and even other kids at school, etc. The result is a ‘guide to life’ with contributions from every human who has ever tried to make him behave.
Remember, humans are born into an ‘alien world’.
Rules reward with pride and happiness when obeyed, and punish with shame and remorse when disobeyed
Humans judge themselves by their Rigid Rules, and so they are too afraid to investigate their minds because they can’t afford to stumble upon unexpected ‘wrong’ thoughts and desires.
17: OBSERVE THE QUARRY – TIME & RESILIENCE
An average human being would consider himself to be the king of his Castle (his mind). Fair enough. More often than not, though, mainly due to incompetence, humans are far from being their own masters. They resemble clown kings, impotent rulers governed by dark forces that they are too afraid to face, even acknowledge.
In general, humans follow the path below:
One: OUTWARD LOOKING
Humans spend their lives looking outwards and repressing dark thoughts.
Two: INNER IGNORANCE
Humans usually refuse to look inwards to understand who they are, their thoughts, what they need and want.
Three: EXCESSIVE COMPARISON & ADAPTATION
18: HUNTING GUIDE – KEY NOTES
- Just codes:
Human don’t express themselves as clearly as they think — their internal system is highly inefficient.
Humans have no idea about how much their words reveal — like when they criticise something.
- Each human’s reality is unique:
Inside the brain:
Every human is like a captain controlling a ship from inside his cabin (isolated dark room). The Messenger translates everything that reaches the Captain. Everything. And, humans confuse information the Messenger supplies with reality. They, in effect, ‘see’ the world with their brains, not eyes. So, humans project reality (hallucinate), and what they believe to be real is highly influenced by Hidden Associations and Drawers.
- Emotions & desires:
- Humans’ lack of an outsider’s point of view:
- Expanded Self-Interest:
- Fear & related feelings:
- Vanity, pride & admiration:
- Rigid Rules:
- Time to observe:
THE LAYER WHERE THE CAPTAIN EXISTS
Squeezed by the Crew
The thin layer where the Captain exists.
1 – Crew – Filters reality that is captured through senses such as eyes and ears.
- Decides the fraction of information to send
- Edits information using Hidden Association and Drawers
- Uses blame and denial whenever necessary
2 – Captain (thin grey circle) – Makes a small amount of the decisions and thinks he is in control.
3 – Crew – Sends emotions and desires back to the Captain while always focused on escaping fear and chasing vanity.
- Manages:
- Organs (heartbeat, body temperature, etc.)
- Emotions and desires
- Repressed memories
- Holy Grail (s)
- Rigid Rules
- Levels of minimum requirements
- Expanded Self-Interest
The Crew judges whether or not the animal is in Survival Mode, getting farther away from or closer to its Holy Grail.
19: THE SUPERIORS – PILOTING THE ANIMAL
Superiors are scarce, enhanced human beings. Although they look like and can interbreed with regular humans, the distance between Superiors and regular humans is greater than that between a human and a chimpanzee.
The characteristics of Superiors.
To become a Superior, a human must undergo an internal separation — a divorce between his Captain and Crew. He must split the parts of himself that he can control from the rest, which he can only train (or tame). By doing so, a human becomes a mere dot inside his head, and he pilots his body like a spaceship.
A Superior recognises that he and what he feels are not the same. Emotions are indicators, not absolute truths. So, a Superior pays attention to and questions his feelings as if monitoring a control panel, and he reacts in a manner that he believes appropriate, not how his Crew wants. Sensations are advisors, not bosses.
Superiors realise that the prey they must observe is, actually, themselves. By exploring their thoughts and emotions, Superiors escape haunting memories and are free to chase the future.
Superiors know that as they gain self-awareness and discover what they want, it makes less sense to become upset by external things that are not real threats. By paying attention to, and destroying wrong Hidden Associations, Superiors slowly break the pattern of angriness commonly seen in humans. Consequently, they hardly ever get annoyed at others; Superiors are secure and robust.
Superiors NEED little and WANT big. They are free.
Superiors don’t have to live in poverty to need little. Having low minimum requirements is a mindset, not a bank balance, and Superiors are, actually, often wealthy. Despite having low minimum requirements, these superhumans still search for the impossible without needing to achieve it.
For a human to become a Superior, he must dedicate himself to introspection and self-development. Also, rather than adopt a pre-packaged super-self courtesy of his social group, a human must create his own with a clear definition of success in mind.
Superiors understand that self-investigation never ends.
With relaxed rules of acceptance, Superiors live in a Zen-like state. They enjoy self-exploration. And, due to the multitude of Hidden Associations humans face every day, it is an endless pursuit, which is the best part.
Superiors plan for the long-term while aware that no human’s lifespan is certain.
A Superior’s definition of happiness is inner peace, not strong feelings.
Remember, humans are, in essence, animals.
Superiors are masters of their minds — superbeings. They are complete and have low needs and well-defined Holy Grails.
AND LAST
Realise that this book is not a guide for hunting humans; rather, it is my quirky explanation for why humans behave in the ways that they do and how their minds work.
This book from the point of view of an outsider — a visitor from another world — which I believe was necessary to expose human characteristics and the problems we all face.
If you liked this book:
- Sign up at HuntingHumans.com to keep in contact and receive updates from us.
- Follow us on Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter.
- Take your time to leave a review with your favourite retailer
BUY THE BOOK HERE
♣CLICK THIS TO STOP TRYING TO ACHIEVE YOUR GOALS BY YOURSELF AND BE COACHED TODAY HERE
♥CLICK THIS TO DOWNLOAD THIS FREE PDF SUMMARY HERE
♦CLICK THESE FOR THE FOLLOWING Book | Summaries | Course
YouTube |Spotify | Instagram | Facebook | Newsletter | Website